The growth in Europe's distribution transformer market is expected to be driven by decarbonization initiatives, renewable energy integration, and EV adoption.
- The growth in Europe's distribution transformer market is expected to be driven by decarbonization initiatives, renewable energy integration, and EV adoption.
- Europe aims for a 45% renewable energy share and 30 million electric vehicles by 2030, necessitating significant grid upgrades and expansions to meet these targets.
- Adoption of ester-based and digital transformers is increasing, enhancing safety, sustainability, and efficiency, while the EU's eco-design directive aims to further reduce energy waste and environmental impact.
Introduction
The global push towards decarbonization, the increased integration of renewable energy, and the electrification of the transport sector are driving significant investments in the power grid. In 2023, global investments in electricity grids reached $331 billion, with Europe contributing 20%. Of Europe's $66 billion investment, nearly 60% was allocated to the distribution network, reflecting the need to update infrastructure that is over 40 years old and not up to current EU standards. Initiatives such as the Recovery and Resilience Plans (€13 billion) and the EU's "Digitalization of the Energy System" action plan ($633 billion by 2030) underscore the commitment to grid modernization.
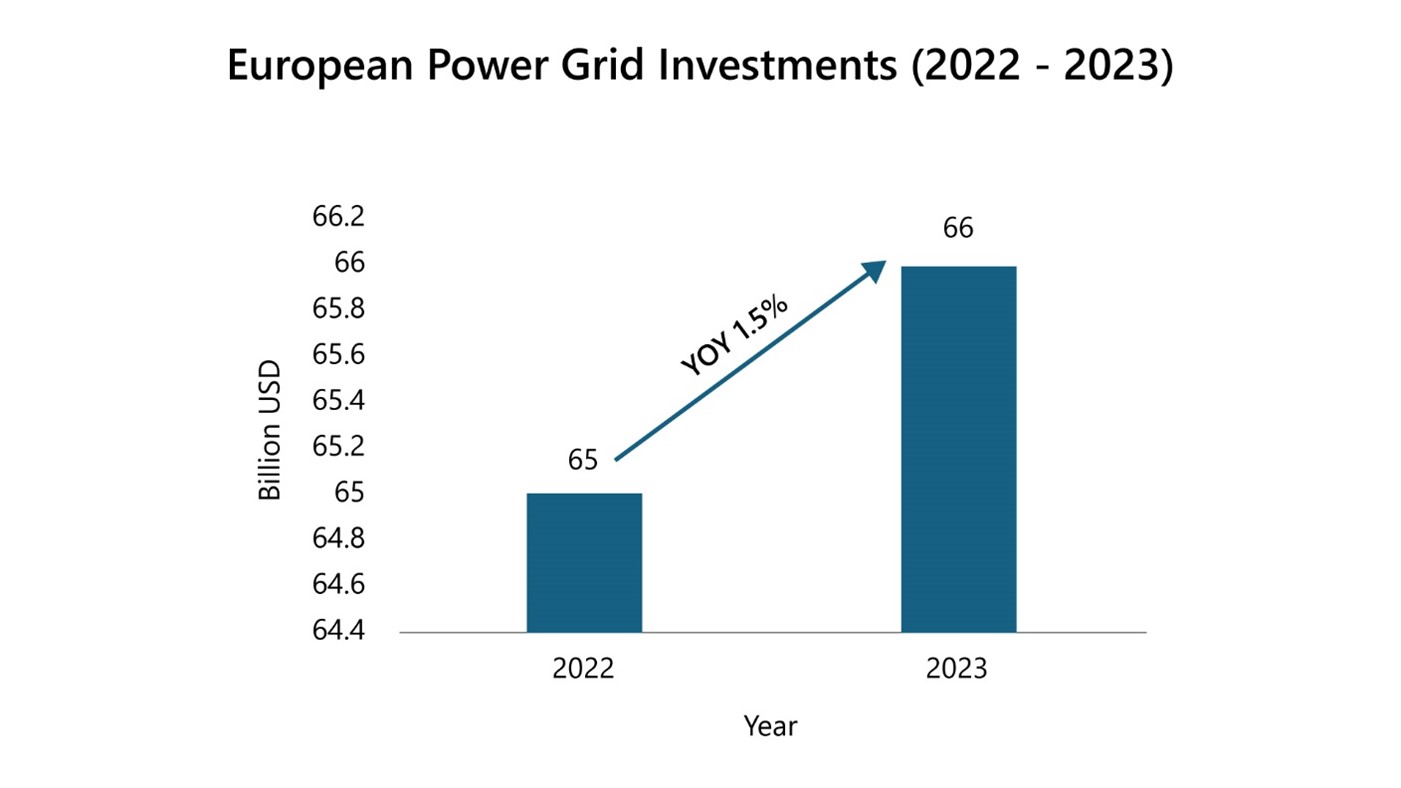
Title: European Power Grid Investments
Source: PTR Inc.
Market Overview: Growth Drivers and Competitive Advantages
The Europe Distribution Transformer (DT) market is poised for significant growth, driven by various factors, including the global push towards decarbonization, increased integration of renewables, and electrification of the transport sector, which necessitate substantial investments in the power grid.
Nearly half of the European DT market operates within the voltage range of 17.5-24kV, predominantly featuring pad-mounted transformers with an average capacity of around 600kVA. This segment plays a crucial role in the distribution network, ensuring efficient and reliable electricity delivery to end-users. The dominance of oil-type transformers in the European market is noteworthy, as they accounted for 82% of the annual market revenue in 2023. These transformers are favored for their durability and cost-effectiveness, making them a staple in the region's electrical infrastructure.
Unlike the U.S. market, which heavily relies on imports to meet its demand, Europe is nearly self-sufficient, producing the majority of its distribution transformers locally. This self-reliance not only enhances the security of supply but also allows Europe to maintain lead times within a 16–18-week timeframe, ensuring timely delivery and installation of transformers. This efficient production capability is a key competitive advantage for the European market.
Geographically, Germany, France, and the UK are the primary markets within Europe, collectively accounting for 40% of the continent's total distribution transformer market. These countries have robust industrial sectors and ambitious renewable energy targets, driving the demand for advanced and reliable transformer solutions. Germany, with its strong focus on renewable energy, particularly solar and wind, leads the market, followed by France and the UK, which are also making significant strides in grid modernization and expansion.
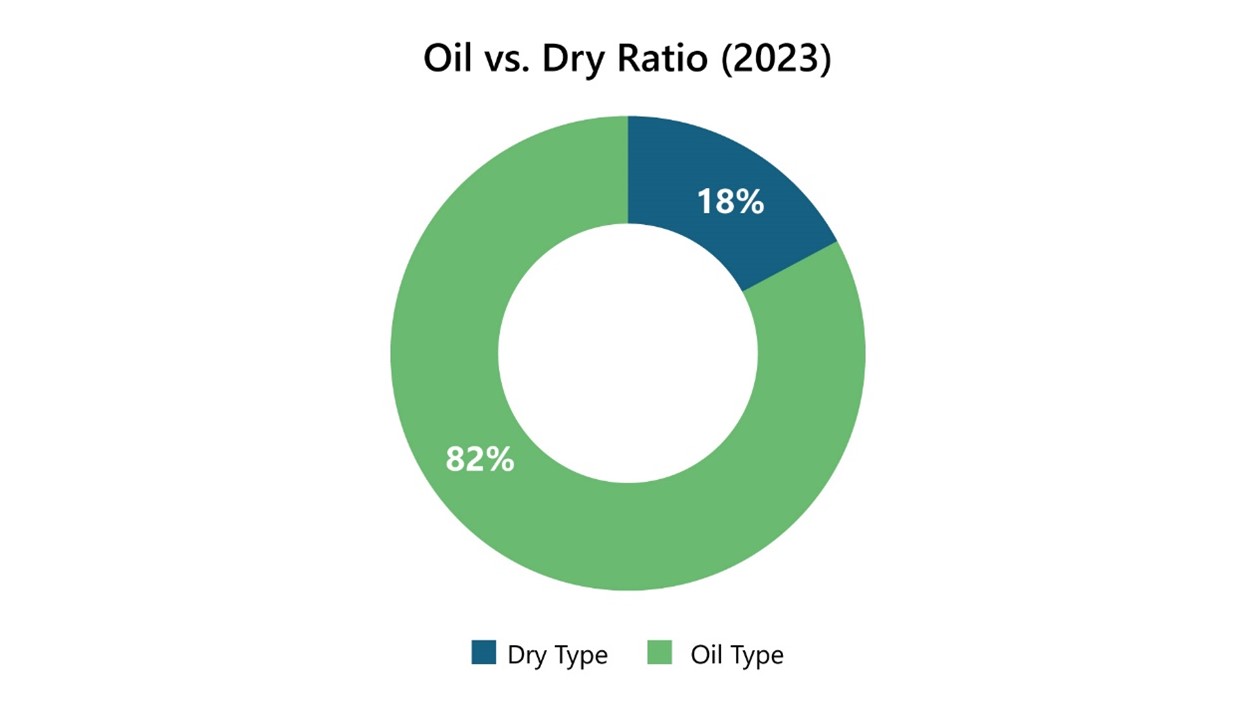
Title: Oil vs. Dry Ratio
Source: PTR Inc.
The Transformative Impact of Europe's Renewable Energy Revolution on the Distribution Transformer Market
Europe's ambitious decarbonization agenda, characterized by aggressive renewable energy targets and the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, is a primary driver behind the growth of the distribution transformer market. The region's push towards integrating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, coupled with the necessity to support electric vehicle charging infrastructure, mandates significant enhancements and expansions of the distribution network. Consequently, there is a burgeoning demand for distribution transformers to facilitate these developments.
Europe has set ambitious goals for renewable energy, aiming to achieve a 45% share by 2030, with targets of 600 GW for solar photovoltaic (PV) and 480 GW for wind energy. Projections from the International Energy Agency (IEA) suggest that between 2024 and 2028, Europe will add 450 GW of renewable energy capacity, with solar PV accounting for over 70% and onshore wind projects contributing 26%.
Despite promising growth in solar PV capacity, Europe faces challenges in meeting its wind energy targets. To reach a 42.5% renewable energy share by 2030, the European Union needs to install more than 30 GW of wind energy annually, yet current additions fall short at approximately 20 GW per year. The hurdles include delays in permitting, grid limitations, under-subscribed auctions, and escalating costs of raw materials.
In response to these challenges, Europe has implemented regulatory reforms aimed at simplifying permitting processes. In 2023, Germany and Spain collectively issued 70% more permits for onshore wind projects compared to the previous year. Brussels introduced the Wind Power Package in December 2023, designed to accelerate growth in the wind industry by streamlining permitting procedures, optimizing auction pricing mechanisms, mitigating inflationary pressures, and investing in critical infrastructure like ports and grid systems.
Several European countries have outlined specific renewable energy targets to contribute to the region's overall goals. Germany, for instance, aims to achieve 100% renewable energy in its energy mix by 2035, with targets of 215 GW for solar PV and 115 GW for wind capacity by 2030. France has set a target of generating 40% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030, aiming for 60 GW of solar PV and substantial expansions in offshore wind capacity. The UK targets 60% renewable electricity generation by 2030, with plans to install 50 GW of offshore wind and 40 GW of solar PV. Spain aims to install 76 GW of solar PV and 62 GW of wind power by 2030, while Italy aims to increase its renewable electricity share to 65% by 2030, expanding its installed capacity to 131 GW, including an additional 80 GW of solar PV.
The Impact of Accelerating EV Adoption
The electrification of transportation marks a pivotal step in Europe's decarbonization efforts. The EU aims to achieve 30 million electric vehicles (EVs) on the roads by 2030, ultimately phasing out gas-powered cars by 2035. This ambitious target is poised to significantly increase the demand for EVs and infrastructure to support their charging needs.
In alignment with these goals, the EU has outlined plans to establish charging stations every 60 kilometers along major highways by 2026, alongside mandates requiring chargers in new constructions. Furthermore, the EU has earmarked €352 million to finance 26 alternative fuel infrastructure initiatives. Notably, Tesla is set to receive €148 million to install more than 7,000 rapid chargers across 687 locations spanning 22 countries.
The widespread adoption of EVs necessitates extensive upgrades to the electrical grid, prompting a surge in demand for distribution transformers. This infrastructure expansion is essential to accommodate the increased electricity consumption associated with charging EVs across Europe.
Eco-design Initiatives
The eco-design directive within the European Union plays a crucial role in advancing sustainability by setting energy efficiency standards for various products. Specifically, it mandates criteria for transformers aimed at minimizing energy losses and enhancing overall efficiency. The directive was initially introduced in 2015 with Tier 1, which aimed to decrease annual losses from 93.4 TWh to 16.2 TWh by 2025. Building on this foundation, Tier 2 was implemented in 2021, targeting an additional 10% reduction in energy wastage compared to Tier 1.
Looking ahead, discussions are currently ongoing for the introduction of Tier 3 of the ECODESIGN directive. This upcoming phase is expected to introduce regulations pertaining to amorphous steel, mirroring recent standards set by the Department of Energy (DOE) in the USA. Implementation of Tier 3 is anticipated by 2027, further reinforcing Europe's commitment to energy efficiency and sustainability in transformer design.
Advancing Transformer Technology: Ester-Based and Digital Innovations in Europe's Drive for Efficiency and Sustainability
Advancements in transformer technology are driving improved performance, enhanced safety standards, and reduced carbon emissions, aligning closely with global decarbonization objectives.
One significant technological shift is the adoption of ester-based transformers, replacing traditional mineral oil variants. Ester-based alternatives offer sustainability advantages, being biodegradable and non-toxic, while also providing superior thermal aging characteristics and higher flash points. Despite their limited initial deployment in Europe, there is a growing trend towards their adoption, particularly evident among UK utilities that have embraced them exclusively.
Within Europe, synthetic ester-based transformers are preferred over natural ones, which are more prevalent in the Americas. Countries like Germany, Sweden, the Netherlands, and Poland lead in their adoption, driven by stringent fire safety regulations. In the Nordic region, ester-based transformers are widely used in renewable energy applications.
Manufacturers are actively responding to this market shift. For instance, Westrafo has allocated 80% of its manufacturing capacity to produce ester-based transformers. Additionally, Shell's acquisition of MIDEL and MIVOLT from M&I Materials underscores the company's strategic focus on capitalizing on the growing market for ester fluids.
Digitalization represents another transformative trend in the transformer industry, enabling the collection and intelligent utilization of data to manage distributed energy sources, including renewables. Europe is at the forefront of embracing digital transformers, commanding 28% of the global market share in 2023.
A survey conducted by PTR indicates that European end-users increasingly prefer advanced digital transformers equipped with features such as remote monitoring and integration with online platforms. This preference underscores their willingness to invest approximately 20% more in transformers with enhanced digital capabilities.
Looking ahead
If you found this article insightful, registration for CWIEME Berlin 2026 is now open. Join the industry’s largest coil winding and electrical manufacturing exhibition to explore how Europe’s distribution transformer market is adapting to the energy transition and go deeper on these topics with peers, suppliers and technical leaders.
Conclusion
Europe's push towards decarbonization, coupled with the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy sources, is driving significant advancements in the region's power grids. Transformers play a critical role in ensuring reliability and efficiency within these evolving grids, although challenges in manufacturing could potentially delay renewable energy initiatives.
In response to these challenges, new technologies are emerging to enhance transformer performance. Digital transformers equipped with smart monitoring systems enable more effective management of electricity distribution networks. Similarly, ester-based transformers are gaining traction due to their superior safety features and sustainability benefits compared to traditional mineral oil transformers.
Furthermore, PTR believes that ongoing discussions surrounding Tier 3 of the eco-design directive underscore Europe's commitment to improving energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact in the transformer industry. These discussions are particularly focused on regulations concerning amorphous steel, which are expected to further advance efficiency standards.
Overall, these developments signify a concerted effort to modernize Europe's power infrastructure, aligning with ambitious environmental goals while ensuring the reliability and sustainability of energy supply.
About PTR: With over a decade of experience in the Power Grid and New Energy sector, PTR Inc. has evolved from a core market research firm into a comprehensive Strategic Growth Partner, empowering clients’ transitions and growth in the renewable energy landscape and E-mobility, particularly within the electrical infrastructure manufacturing space.
About the Author
Analyst - PTR Inc.
 Eyman is an Analyst at PTR Inc., where she specializes in Transformers topics. Her professional journey began in the research sector at IDR, where she worked as a Market Research Analyst for the APAC region. After gaining a year of valuable experience analyzing market trends across various domains, Eyman moved to PTR as a Power Grid Analyst. Currently, her focus is on conducting thorough analyses and providing insights into the field of Transformers. Eyman has a strong technical background, having earned a bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering.
Eyman is an Analyst at PTR Inc., where she specializes in Transformers topics. Her professional journey began in the research sector at IDR, where she worked as a Market Research Analyst for the APAC region. After gaining a year of valuable experience analyzing market trends across various domains, Eyman moved to PTR as a Power Grid Analyst. Currently, her focus is on conducting thorough analyses and providing insights into the field of Transformers. Eyman has a strong technical background, having earned a bachelor’s degree in electrical engineering.
Contact: