Smart EV Charging: A Deep Dive into Distributed Architecture and Dynamic Load Management
by Amna Mumtaz, Analyst I – at PTR Inc.
- The electric vehicle (EV) sector is currently undergoing a substantial shift, with the introduction of two cutting-edge technologies: distributed architecture and dynamic load management.
- Unlike traditional centralized systems, distributed architecture employs a network of interconnected charging points, providing scalability, flexibility, redundancy, and cost-effective expansion.
- Dynamic load management focuses on optimizing electrical power distribution during charging sessions, providing benefits such as grid stability, enhanced user experience, and balancing power distribution.
The electric vehicle (EV) sector is undergoing a substantial shift, with advancements in charging infrastructure taking on a central role. Two cutting-edge technologies, distributed architecture and dynamic load management, are at the forefront of this revolution, making smart EV charging a practical reality. This article explores these technologies in detail and their impact on the EV landscape.
Distributed Architecture
Distributed architecture, also known as decentralized charging, represents a fundamental shift in the EV charging industry. Unlike traditional centralized systems, this approach employs a network of interconnected charging points, providing scalability, flexibility, redundancy, and cost-effective expansion.
Scalability
The most significant advantage of distributed architecture is its exceptional scalability. As the number of EVs on roads continues to increase, the demand for charging infrastructure grows in tandem. With distributed systems, additional charging points can be effortlessly integrated into the network, accommodating the increasing EV population without requiring costly and time-consuming infrastructure upgrades.
Flexibility
Another important advantage of distributed architecture is flexibility. Charging stations can be strategically deployed in diverse locations, from private residences and workplaces to public parking lots and highways. This flexibility ensures EV users can charge wherever and whenever needed, making EV ownership more practical and convenient.
Redundancy
Reliability is a cornerstone of EV charging, and distributed architecture excels in this regard. The interconnected nature of the charging network means that if one charging point encounters technical issues or requires maintenance, other charging stations or charging points within the network can seamlessly take over, minimizing disruptions to EV users. This built-in redundancy enhances the overall dependability of the charging infrastructure.
Cost-effective expansion
Traditional centralized charging systems can be expensive to expand, especially as demand grows. Distributed architecture addresses this concern by minimizing the need for extensive cabling and infrastructure. This cost-effectiveness is pivotal in rapidly expanding the charging network, making it a practical solution for widespread adoption.
The distributed architecture of EV chargers represents a paradigm shift in electric mobility. Its scalability, flexibility, redundancy, and cost-effectiveness make it a promising solution for the future of EV charging infrastructure. As more EVs hit the road, embracing distributed architecture will be instrumental in creating a seamless and sustainable charging ecosystem, empowering individuals to switch to cleaner, more efficient transportation.
Dynamic Load Management
Dynamic load management is a critical component of the smart EV charging ecosystem, focusing on optimizing electrical power distribution during charging sessions.
DLM represents an intelligent software solution engineered for efficiently managing energy allocation within a concurrently operating multiple electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. DLM dynamically oversees and optimizes the distribution of the available power among the EV chargers, providing the flexibility to tailor power allocation according to specific operational requirements. DLM offers multiple benefits, such as grid stability and integration, enhanced user experience, and balancing power distribution, to name a few.
Grid stability and integration
DLM actively contributes to grid stability by intelligently distributing power to charging stations and preventing grid overloads during peak demand. This enhances grid reliability and minimizes the risk of power outages.
Moreover, DLM facilitates the seamless integration of EV charging infrastructure with the broader electrical grid. This integration promotes a smoother transition to sustainable energy sources, allowing EVs to provide grid services, balance energy demand, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and enhance overall grid efficiency.
Balancing power distribution
DLM dynamically allocates electrical power among multiple charging points within a network. This intelligent distribution optimizes charging times and ensures that each EV receives the required power.
Cost savings
One of the most significant advantages of DLM is its potential for cost savings. Optimizing power distribution helps reduce high-demand charges for EV owners and charging station operators, resulting in more affordable charging for users and cost-effective operation for charging networks.
Enhanced user experience
DLM ensures that EV users enjoy an enhanced charging experience, whether they are at home, work, or a public charging station. This means users can count on a reliable and smooth charging process without encountering voltage disruptions or unexpected power fluctuations.
Adaptive and future-proof
DLM is adaptive and future-proof, capable of evolving with the changing landscape of EV charging. As there are advancements in EV technology and power demands evolve, DLM can adjust to meet new requirements, ensuring its continued value in intelligent charging infrastructure.
Scalability and flexibility
DLM offers both scalability and flexibility for charging infrastructure. As the demand for commercial EV charging stations increases, the system can efficiently allocate power resources, ensuring not only effective operation but also seamless expansion to accommodate growing needs.
Equitable distribution
DLM offers the flexibility to distribute energy equitably or prioritize specific EV chargers based on occupancy. This ensures fairness in charging access and efficient power utilization.
Remote monitoring
DLM allows for real-time remote monitoring, providing detailed power consumption information for efficient energy management.
Building management system (BMS) integration
DLM integrates with building management systems (BMS) and other monitoring software. This integration enhances energy management, efficiency, and grid overload prevention within the existing infrastructure. Incorporating dynamic load management into EV charging addresses key challenges and paves the way for a more sustainable, efficient, and user-friendly electric mobility ecosystem.
DLM is helpful as it provides multiple advantages to the electric grid infrastructure and EV consumers. The impact of DLM compared to no or static load management is shown in the figure below.
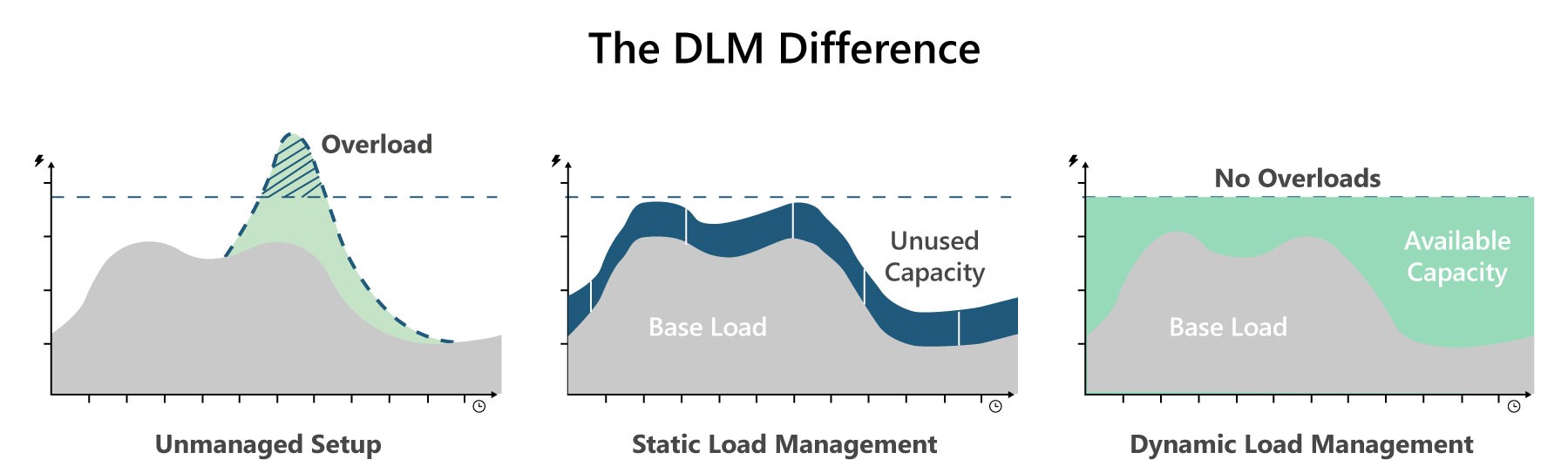
Figure 1: Comparison of Unmanaged Setup with Static Load Management and Dynamic Load Management. Source: gridX
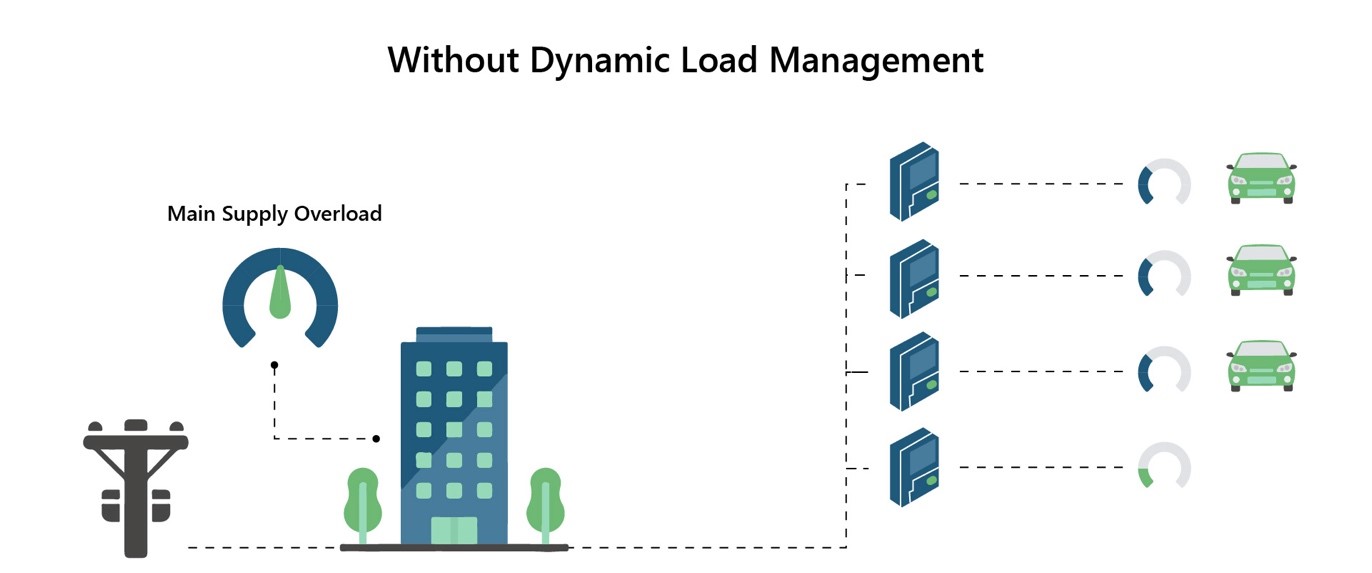
Figure 2: Charging EVs without Dynamic Load Management Technology. Source: circontrol
Looking Ahead
Dynamic load management (DLM) shines brightest within a distributed architecture framework, which is why a shift is being observed in the EV industry towards these cutting-edge technologies that provide a range of benefits (discussed earlier in detail). Dynamic load management can be effectively implemented in all-in-one and distributed architecture EV chargers. While all-in-one chargers excel at optimizing efficiency for individual stations, distributed architecture chargers offer broader grid stability benefits and adaptability for network expansion.
PTR believes that as economies push for widespread adoption of EVs, technologies such as dynamic load management and decentralized charging will have a crucial role to play as they provide a potent blend of efficiency, scalability, grid friendliness, and cost-effectiveness.

About the author
Amna works as a market analyst in PTR's EVCI team. She graduated with an MS in Electrical Engineering from NUST, where she was the top achiever with the highest CGPA in the 2022 MS EE batch. Amna's expertise lies in conducting market research for EV chargers in the APAC region, making significant contributions to the e-mobility department.